A Gartner study found that successful organizations are 1.6x more likely to establish clear strategies and goals. When working to achieve goals, KPIs serve as the compass, guiding you toward your objective and providing invaluable insights into various facets of operations.
With so many metrics available, you might find it challenging to determine which KPIs deserve your attention. In this article, we explore essential key performance indicators examples that every business needs to measure, highlighting their significance and impact on organizational growth and sustainability.
Table of contents:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are quantifiable metrics used by organizations to assess their performance in achieving specific goals and objectives. These measurable values span across various facets of business operations, such as financial performance, customer satisfaction, employee productivity, and operational efficiency.
KPIs are vital tools for evaluating progress, identifying areas for improvement, and making data-driven decisions. By tracking and analyzing these metrics through a KPI dashboard (or Liveboards as we call them), businesses can effectively monitor their performance, align activities with strategic objectives, and drive continuous improvement to ensure long-term success and competitiveness in their respective industries.
The finance department is responsible for managing financial data within a company. Key players in this department include financial analysts, accountants, and financial managers. They often rely on comprehensive financial Liveboards to track and analyze key metrics for informed decision-making and performance management.
Financial KPI examples include:
Revenue growth rate: The revenue growth rate measures the percentage increase in a company's revenue over a specific period. This metric is crucial for evaluating your company’s ability to generate more sales and expand its market presence. By tracking the revenue growth rate, you can assess the effectiveness of your sales and marketing strategies and pinpoint areas for improvement.
Gross profit margin: Gross profit margin represents the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold (COGS). It helps you measure the efficiency of your production and pricing strategies, as well as your ability to generate profits from your core business activities. A higher gross profit margin indicates that you can retain more revenue after accounting for the direct costs associated with producing goods or delivering services.
Net profit margin: Net profit margin represents the percentage of revenue that remains as net profit after deducting all expenses, including COGS, operating expenses, taxes, and interest. It helps you understand the overall profitability of your operations, taking into account all expenses incurred to generate revenue. A higher net profit margin signifies that you are able to generate more profit from each dollar of revenue.
Projected revenue: Projected revenue is the estimated total income that a company anticipates generating within a specific future period, often a fiscal year or quarter. It plays a critical role in financial planning and forecasting, providing insights into your company's expected financial performance and helping to guide strategic decision-making.
🔍Here are 21 financial KPIs and metrics you should track in 2024
Marketing involves activities aimed at promoting products or services, building brand awareness, and driving prospect engagement for sales. It encompasses various channels such as advertising, digital marketing, public relations, and market research. Marketers rely on sophisticated marketing Liveboards to monitor and analyze key metrics, enabling data-driven decision-making and campaign optimization.
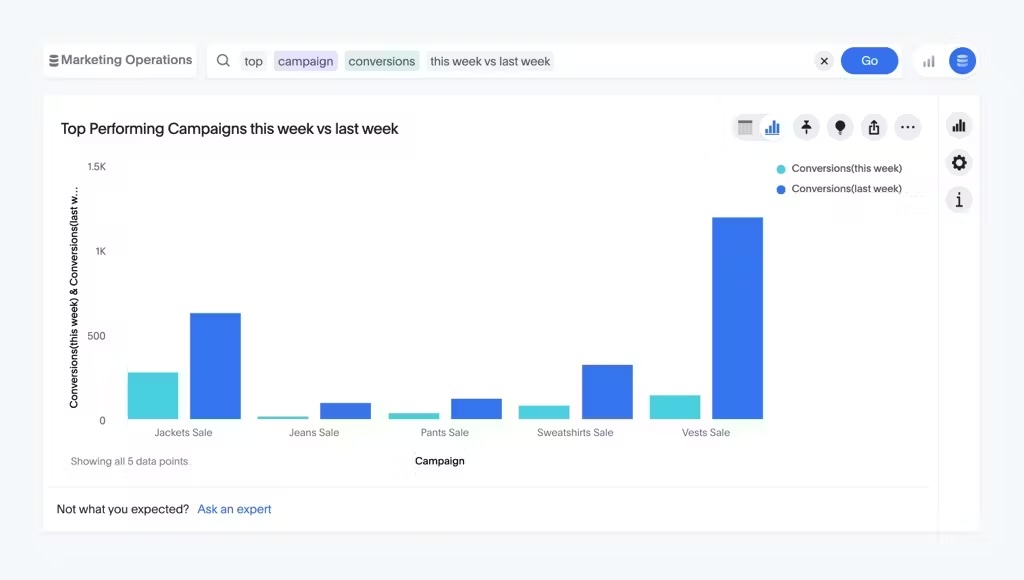
Marketing KPI examples include:
Customer acquisition cost (CAC): Customer acquisition cost measures the cost incurred to acquire a new customer. It provides valuable insights into the efficiency of your marketing campaigns and aids in budget allocation.
Customer lifetime value (CLTV): Customer lifetime value estimates the total revenue a customer is expected to generate over their entire relationship with the company. This estimation guides customer segmentation and retention strategies.
Conversion rate: The conversion rate tracks the percentage of website visitors or leads who take a desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter. Analyzing conversion rates helps identify areas for improvement in the sales funnel and enhances overall campaign performance.
Return on advertising spend (ROAS): ROAS calculates the revenue generated from advertising campaigns relative to the cost of those campaigns. You can gain insights into the profitability and efficiency of your marketing efforts.
Website traffic: Website traffic measures the volume of visitors to a website. It includes metrics such as total visits, unique visitors, and page views, providing insights into the effectiveness of SEO efforts, content marketing, and online advertising initiatives.
🔍15 marketing KPIs and metrics to track in your dashboard
Sales encompass the process of identifying, prospecting, and converting leads into customers through communication and relationship-building efforts. Sales teams play a pivotal role in driving revenue growth and expanding market share for businesses across various sectors. Utilizing a comprehensive sales Liveboard, you can monitor key performance indicators in real-time.
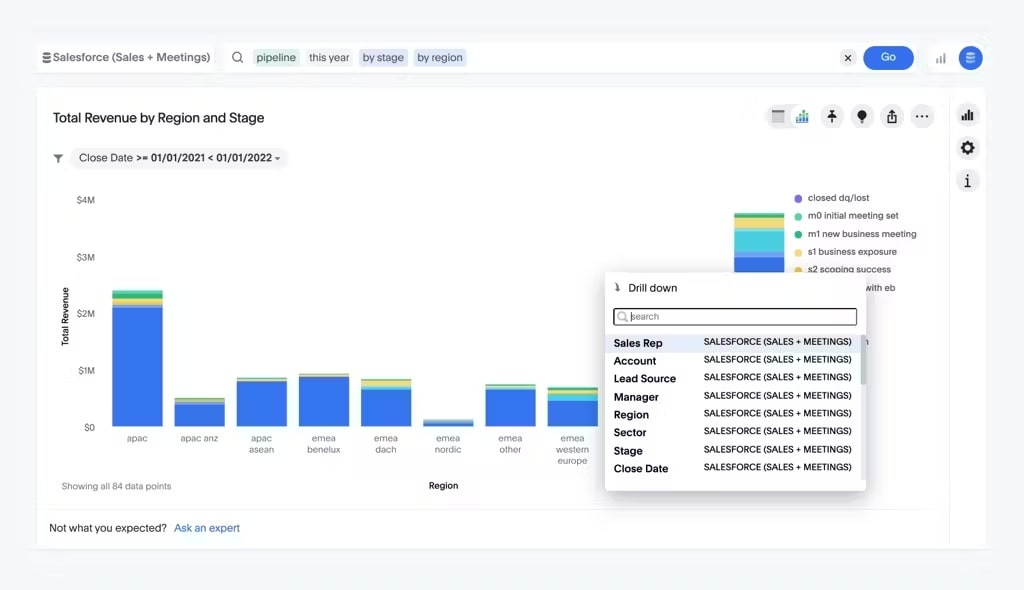
Sales KPI examples include:
Monthly sales growth: Monthly sales growth measures the percentage increase or decrease in sales revenue from one month to the next. It provides insights into the short-term sales performance of your company.
Average profit margin: Average profit margin calculates the percentage of revenue that translates into profit after accounting for all costs and expenses. It indicates the efficiency of your operations in generating profits from its sales.
Monthly sales bookings: Monthly sales bookings represent the total value of sales orders or contracts secured within a specific month. This KPI reflects your sales team's ability to generate new business and close deals within a given period. It provides visibility into your company's revenue pipeline and helps forecast future revenue streams.
Sales opportunities: Sales opportunities refer to qualified leads or prospects in the sales pipeline that have the potential to be converted into customers. This KPI helps sales teams prioritize their efforts and focus on prospects with the highest likelihood of closing a sale.
Sales targets: Sales targets represent the specific, measurable goals set for sales teams to achieve within a given period. These targets are typically based on revenue or sales volume objectives and are aligned with the overall business objectives.
🔍 Top 16 KPIs and metrics every sales team should be tracking in 2024
The Human Resources (HR) function within organizations is responsible for managing various aspects of the employee lifecycle, including recruitment, onboarding, training, performance management, compensation, and employee relations. HR plays a vital role in attracting and retaining talent, fostering a positive work culture, and ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations. To efficiently monitor and analyze these multifaceted responsibilities, HR departments often utilize tools such as HR dashboards.
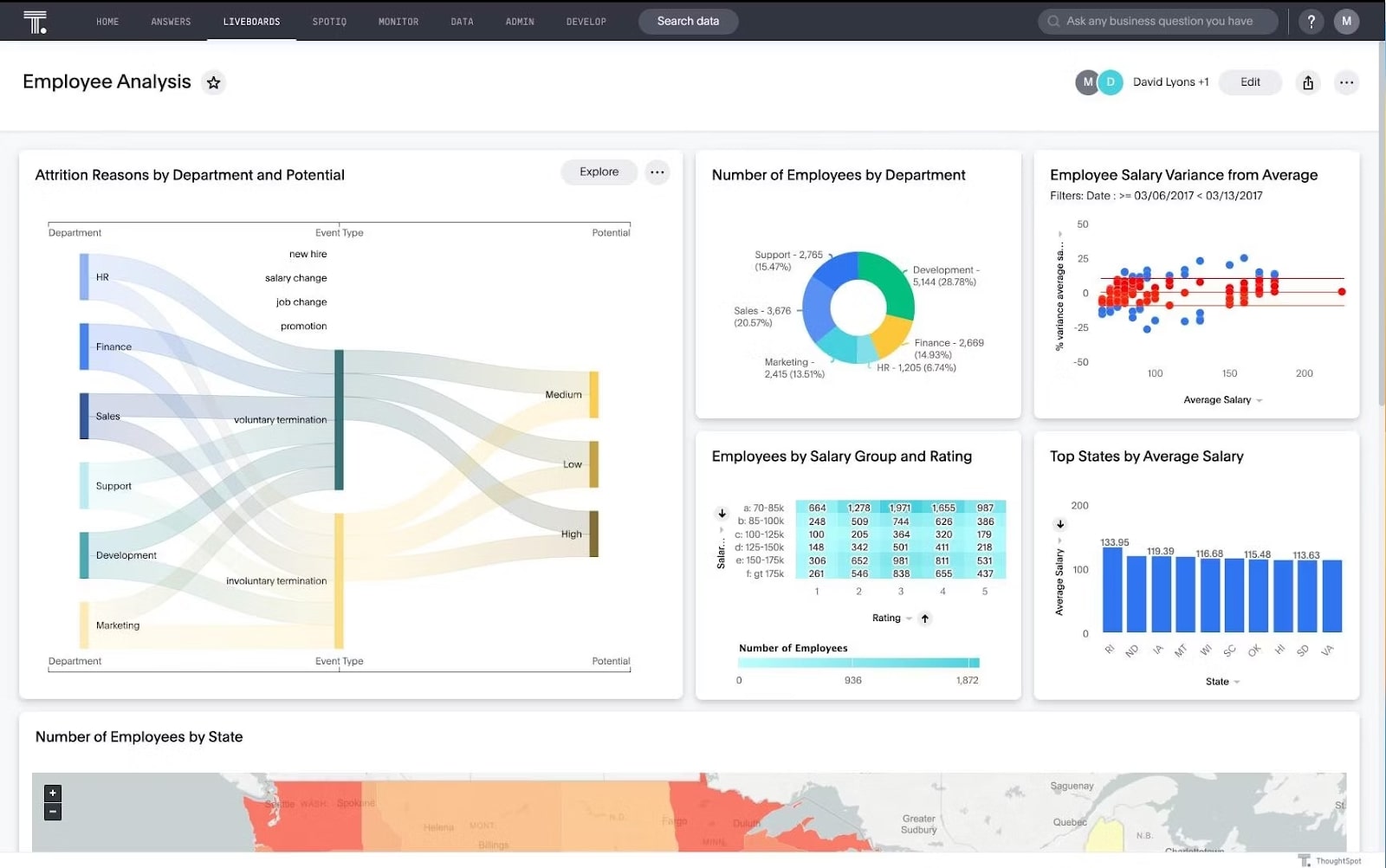
HR KPI examples include:
Employee turnover rate: Employee turnover rate measures the percentage of employees who leave the organization within a specific period. This indicates workforce stability, engagement levels, and the effectiveness of retention strategies.
Employee satisfaction score: Employee satisfaction score surveys or assessments measure employee satisfaction and engagement levels. These provide insights into organizational culture, leadership effectiveness, and areas for improvement.
Time-to-hire: Time-to-hire calculates the average duration from posting a job vacancy to hiring a suitable candidate. It reflects recruitment efficiency and the organization's ability to attract top talent.
Training and development ROI: Training and development ROI evaluates the return on investment from training and development initiatives. It helps in assessing the impact on employee performance, productivity, and skill development.
HR-to-employee ratio: The HR-to-employee ratio compares the number of HR staff to the total number of employees, indicating HR department efficiency and workload distribution.
🔍12 HR metrics examples and KPIs you should track
Operations management focuses on the efficient production and delivery of goods and services. It involves optimizing processes, managing supply chains, and ensuring that operations run smoothly to meet customer demands. Operations teams often use Liveboards to track and analyze performance metrics for continuous improvement.
Operations KPI examples include:
Operational efficiency: Operational efficiency measures the effectiveness of operations in converting inputs into outputs. It helps in assessing the overall productivity and performance of operational processes.
Inventory turnover: Inventory turnover indicates how often inventory is sold and replaced over a specific period. It helps manage stock levels and understand sales patterns.
Order fulfillment time: Order fulfillment time tracks the average time taken from receiving an order to delivering it to the customer. This KPI assesses the efficiency of the order processing and delivery system.
Quality control metrics: Quality control metrics measures the number of defects or errors in products or services. Helps in evaluating the effectiveness of quality management processes.
Customer service focuses on delivering support and assistance to customers before, during, and after a purchase. It plays a crucial role in ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty. Customer service teams use various metrics to evaluate performance and identify areas for improvement.
Customer service KPI examples include:
Customer satisfaction score (CSAT): The CSAT score is the measure of customers' satisfaction with a product or service based on their feedback.
Net promoter score (NPS): The NPS score assesses the likelihood of customers recommending a company’s products or services to others.
First response time: First response time is the track of the average time taken for customer service teams to respond to a customer's initial inquiry.
Resolution time: Resolution time is the measure of the average time taken to resolve a customer issue or complaint.
Product development focuses on creating new products and improving existing ones. It involves research, design, testing, and launching new products to meet market demands and drive innovation. Product development teams track various metrics to ensure the successful delivery of products.
Product development KPI examples include:
Time-to-market: Time-to-market is the time taken from product conception to its launch in the market. It helps in assessing the efficiency of the product development process.
Product defect rate: Product defect rate is the percentage of products that fail to meet quality standards. You can assess the effectiveness of quality control during development.
Customer feedback score: Customer feedback score is the input from customers regarding the product’s features and performance to guide future improvements.
Information Technology (IT) focuses on managing technology infrastructure, software, and data systems within an organization. IT professionals monitor various KPIs to ensure system reliability, security, and efficiency.
IT KPI examples include:
System uptime: System uptime is the percentage of time that IT systems and applications are operational and available.
Incident response time: Incident response time measures the average time taken to respond to and resolve IT incidents or issues.
IT support ticket resolution time: IT support ticket resolution time is the average time taken to resolve support tickets submitted by users.
Data breach incidents: Data breach incidents are the number of security breaches affecting company data, highlighting the effectiveness of security measures.
The Software as a Service (SaaS) industry revolutionizes software delivery by providing cloud-hosted applications on a subscription basis. Within this industry, tracking KPIs is essential for evaluating performance and guiding strategic decision-making. These metrics enable SaaS companies to optimize their operations and drive sustainable growth.
Examples of KPIs in this industry include:
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR): Monthly recurring revenue measures the predictable revenue generated from subscription fees on a monthly basis, providing insights into revenue stability and growth trajectory.
Churn rate: The churn rate tracks the percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions within a specific period. This indicates customer satisfaction, product-market fit, and the effectiveness of customer success efforts.
Average revenue per user (ARPU): Average revenue per user determines the average revenue generated from each user or customer. It aids in pricing strategies, upselling efforts, and revenue forecasting.
Gross margin: Gross margin calculates the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). This metric reflects the profitability of SaaS offerings and operational efficiency.
Customer satisfaction score (CSAT): Customer satisfaction score surveys customers to assess their satisfaction levels with the SaaS product and service. It provides actionable feedback for product enhancements, support improvements, and customer retention initiatives.
🔍12 key SaaS metrics and KPIs you should track in 2024
In the supply chain industry, KPIs play a vital role in evaluating the efficiency, effectiveness, and performance of various processes and stakeholders involved in the supply chain network. These KPIs provide valuable insights into factors such as inventory management, order fulfillment, supplier performance, transportation efficiency, and overall supply chain costs.
Examples of KPIs in this industry include:
Order fill rate: Order fill rate measures the percentage of customer orders fulfilled completely from available inventory, indicating efficient inventory management and customer satisfaction.
Perfect order rate: Perfect order rate reflects the percentage of orders delivered without errors or defects. It showcases operational excellence and enhances customer trust and loyalty.
On-time delivery: On-time delivery measures the percentage of customer orders delivered according to the promised delivery date, demonstrating reliability and responsiveness to customer needs.
Cycle time: Cycle time calculates the average duration required to complete a specific process within the supply chain. It highlights operational efficiency and identifies areas for improvement.
Inventory turnover: Inventory turnover indicates how quickly inventory is sold or used up, reflecting the efficiency of inventory management and minimizing carrying costs.
🔍15 supply chain KPIs and metrics you should track in 2024
The manufacturing industry is characterized by complex processes, high-volume production, and stringent quality standards. In such an environment, key performance indicators are crucial for monitoring and optimizing operational efficiency, quality control, and cost management. KPIs enable manufacturers to identify bottlenecks, improve production processes, and enhance overall productivity. These metrics are typically displayed on a manufacturing Liveboard, providing real-time visibility into performance and facilitating informed decision-making.
Examples of KPIs in this industry include:
Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE): Overall equipment effectiveness measures the efficiency of manufacturing equipment by assessing availability, performance, and quality. It helps in identifying opportunities for downtime reduction and productivity improvement.
First pass yield (FPY): First pass yield calculates the percentage of products manufactured correctly on the first attempt without rework or defects. This indicates process reliability, quality control effectiveness, and waste reduction.
Defect rate: Defect rate tracks the percentage of defective products or components produced within a specific period, highlighting quality issues, root causes, and areas for corrective action.
Production cost per unit: Production cost per unit calculates the total cost of production divided by the number of units manufactured, providing insights into cost efficiency, profitability, and pricing strategies.
Inventory turnover rate (ITR): The inventory turnover rate evaluates how quickly inventory is sold or used within a specific period.
🔍12 manufacturing KPIs and metrics you need to track in your dashboard
In the healthcare industry, where patient outcomes and quality of care are paramount, KPIs play a pivotal role in measuring and improving clinical effectiveness, operational efficiency, and patient satisfaction. The metrics are often visualized on a healthcare Liveboard, offering comprehensive insights into performance and facilitating proactive management of healthcare operations.
Examples of KPIs in this industry include:
Patient satisfaction score: The patient satisfaction score measures patient perceptions of the quality of care, communication with healthcare providers, and overall experience, influencing patient retention, loyalty, and reputation.
Cost per procedure: Cost per procedure measures the average cost incurred by the healthcare facility for performing a specific medical procedure. It provides insights into resource utilization, cost containment strategies, and pricing structures.
Average revenue per patient: Average revenue per patient KPI calculates the average revenue generated by each patient during their interaction with the healthcare facility. Analyzing average revenue per patient helps in understanding the financial impact of patient interactions on the organization.
Revenue cycle length: Revenue cycle length tracks the average duration from patient encounter to reimbursement receipt. Monitoring revenue cycle length helps in identifying inefficiencies and bottlenecks in revenue cycle management.
Employee turnover rate: Employee turnover rate KPI measures the percentage of employees who leave the healthcare organization within a specific period. Analyzing employee turnover rate helps in workforce management, talent retention, and organizational performance assessment.
🔍15 healthcare KPIs & metrics you should track in 2024
The e-commerce industry involves buying and selling goods or services online, facilitated by digital platforms and electronic transactions. KPIs in this industry are essential for evaluating and optimizing various aspects of online business operations. By monitoring e-commerce KPIs, businesses can assess the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, website performance, and customer engagement strategies. These metrics are typically displayed on an e-commerce Liveboard, providing real-time analytics and facilitating data-driven decision-making to drive business growth and profitability.
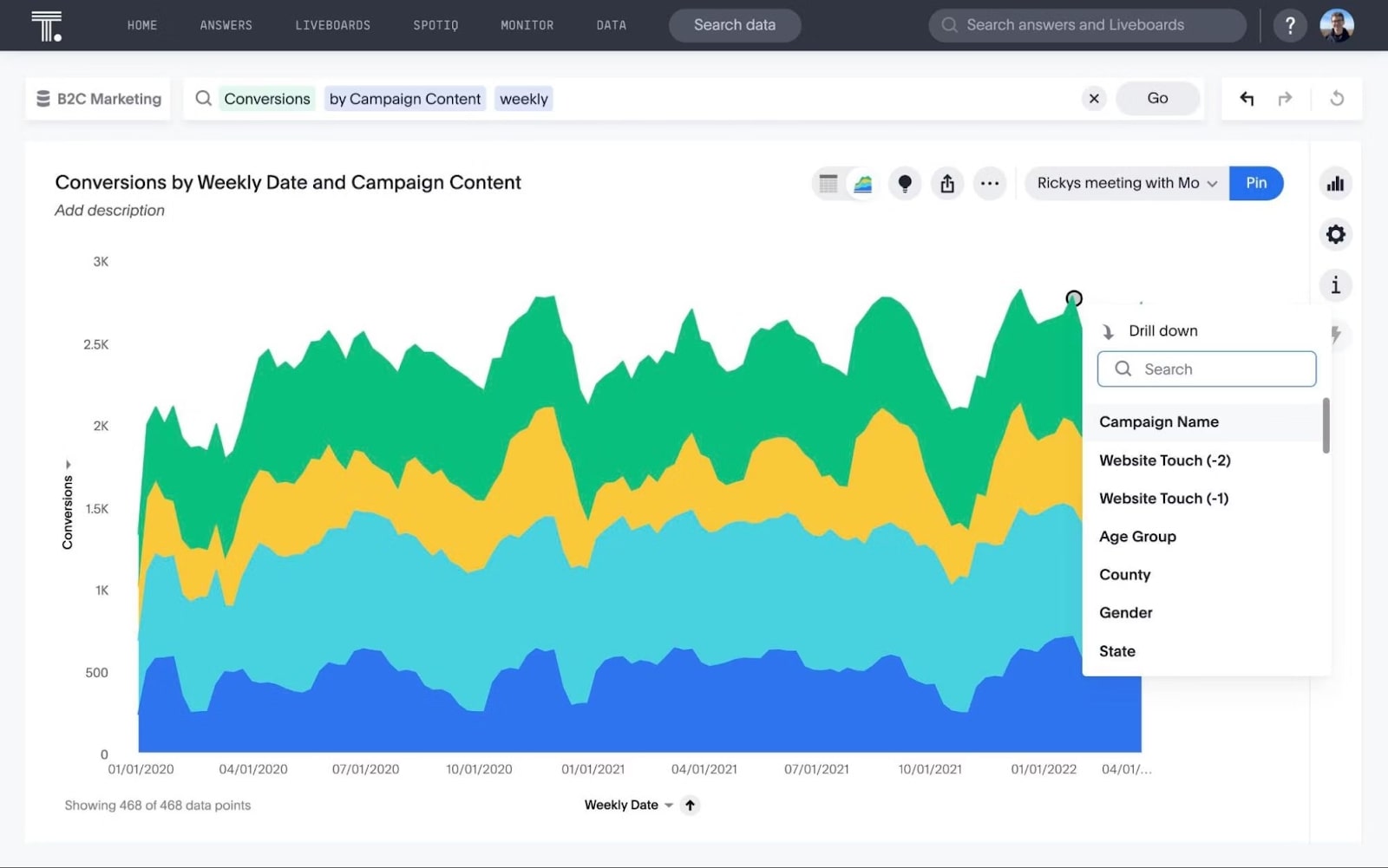
Examples of KPIs in this industry include:
Average order value (AOV): AOV measures the average amount spent by customers in a single transaction.
Cart abandonment rate: This measures the percentage of users who add items to their shopping cart but do not complete the purchase. A high abandonment rate indicates potential issues with the checkout process or pricing.
Retention rate: Retention rate measures the percentage of customers who return to make a repeat purchase. It helps gauge customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Average session duration: The average session duration metric tracks the average amount of time visitors spend on your website during a single session. Longer session durations can indicate higher engagement and interest in your products or content.
Average customer service response time: This metric tracks the average time it takes for customer service representatives to respond to inquiries or support tickets. A fast response time contributes to better customer satisfaction and retention.
In the retail industry, where consumer preferences and market trends constantly evolve, key performance indicators are indispensable for monitoring and optimizing store performance, sales effectiveness, and customer satisfaction. By analyzing these indicators, retailers can identify sales trends, assess store profitability, and optimize merchandise assortments.
These metrics are usually displayed on a dynamic retail Liveboard, offering comprehensive insights into store performance.
Examples of KPIs in this industry include:
Sales revenue: Sales revenue is the total amount of money earned from selling goods or services over a specific period. It's a fundamental measure of a retail business's financial health.
Sell-through rate: The sell-through rate is the percentage of inventory that is sold compared to the total available inventory. It helps retailers identify slow-moving or obsolete products.
Employee productivity: Employee productivity measures the sales generated per employee or per labor hour. It helps evaluate staffing levels and employee performance.
Online sales metrics: Online sales metrics are various metrics related to e-commerce performance, such as website traffic, conversion rate, average order value, and bounce rate. They provide insights into online customer behavior and website effectiveness.
Foot traffic: Foot traffic is the number of people who enter a physical store within a specific period. It's a measure of store popularity and can help assess the effectiveness of location and marketing efforts.
In the telecommunications industry, KPIs are essential for measuring service quality, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. With rapid technological advancements and growing customer expectations, telecom companies must leverage these metrics to stay competitive and ensure optimal performance. KPIs help telecom operators monitor network performance, customer interactions, and financial health, enabling them to enhance service reliability, address customer concerns proactively, and make data-driven decisions.
Examples of KPIs in this industry include:
Average revenue per user (ARPU): ARPU is the average revenue generated from each customer over a specific period. It helps assess revenue generation and guide pricing strategies.
Customer churn rate: Customer churn rate is the percentage of customers who discontinue their services within a given period. A high churn rate may indicate issues with service quality or customer satisfaction.
Network availability: Network availability is the percentage of time the network is operational and accessible to users. It reflects the reliability and stability of the network.
Call drop rate: The call drop rate indicates the percentage of calls that are disconnected unexpectedly. This metric helps identify network issues and improve service quality.
Customer satisfaction score (CSAT): The CSAT score assesses customer satisfaction with service quality and support. It provides insights into customer perceptions and areas for improvement.
In the transportation and logistics sector, KPIs are essential for optimizing the movement of goods and services across supply chains. These metrics offer insights into the efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of logistics operations. By monitoring KPIs, organizations can identify and address bottlenecks, reduce operational costs, and improve service delivery. Effective KPI tracking helps transportation and logistics companies meet delivery deadlines, manage resources efficiently, and enhance overall customer satisfaction in an increasingly complex and fast-paced industry.
Examples of KPIs in this industry include:
On-time delivery rate: On-time delivery rate measures the percentage of deliveries completed by the promised date. This KPI indicates the efficiency and reliability of the delivery process.
Warehouse productivity: Warehouse productivity is a KPI that assesses the efficiency of warehouse operations, including inventory management, picking, and packing processes.
Transit time: Transit time is the average time taken to move goods from the origin to the destination. Shorter transit times can improve customer satisfaction and supply chain efficiency.
Delivery cost per order: Delivery cost per order is the average cost incurred for each delivery. It helps in evaluating cost efficiency and identifying areas for cost reduction.
As businesses evolve in response to shifting market dynamics, the strategic utilization of key performance indicators becomes increasingly vital. By embracing a culture of performance measurement and leveraging advanced analytics tools, you can effectively capitalize on opportunities and navigate challenges. This helps in maintaining a competitive edge in an ever-evolving business landscape.
ThoughtSpot stands at the forefront of this journey, offering transformative analytics solutions. Harness the power of data-driven insights for strategic decision-making and operational excellence—schedule a demo today.









